12
Aug
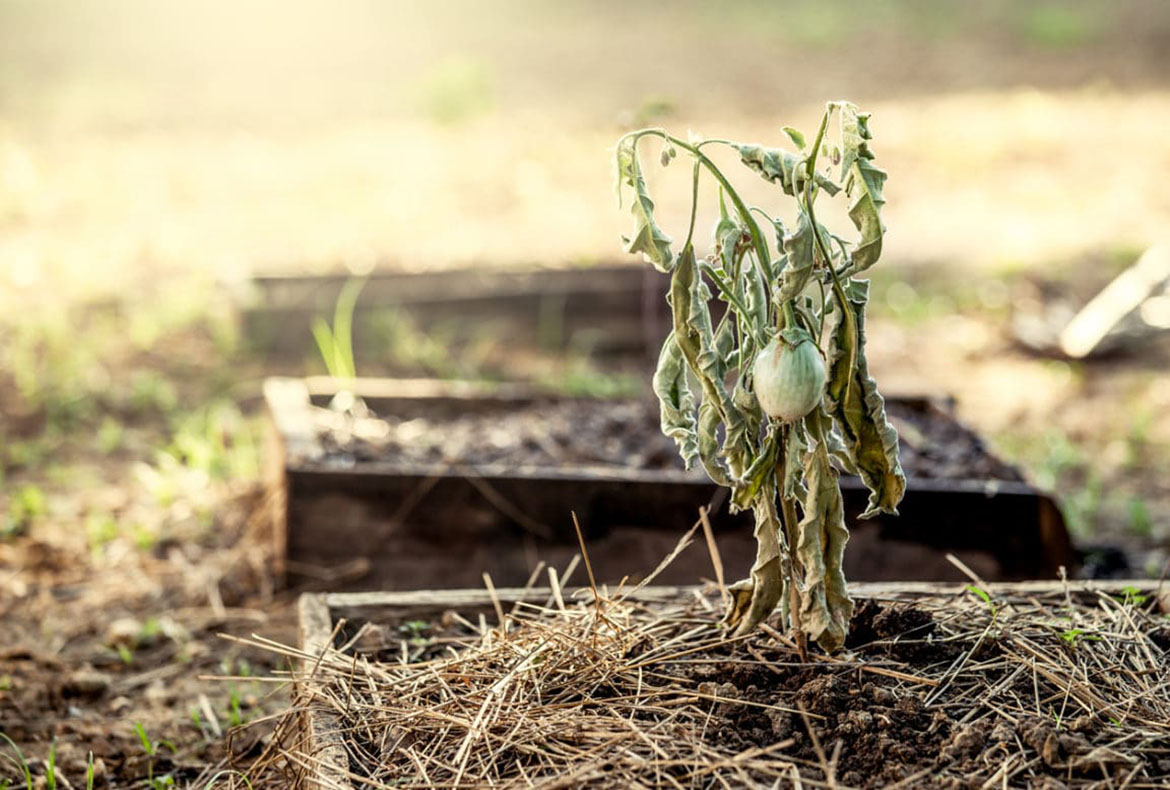
The heat wave causes “vegetation accidents” in the gardens which manifest themselves in unpleasant surprises:
- parched edges of the garden
- bare tree branches
- split tomatoes
- “burnt” leaves
- cracked floors
An alert occurs when daytime temperatures exceed 33–34°C and nighttime temperatures do not drop below 20°C.
In these thermal conditions, the garden is subjected to a very important evaporation which harms the growth and the health of all the vegetable cultures.
RELEVANT POSITIVE SOLUTIONS
- choose the right plants and the right varieties resistant to drought,
- plan watering with a microporous hose (a sprinkler system that helps maintain soil moisture thanks to the water droplets that slowly escape through the pores of the hose). This mobile system can be moved from one crop to another and squeeze between rows of planting. This system prevents the soil from drying out, wasting water, and the formation of an earth crust.
- cover the soil of the vegetable garden with a mulch. This must be the first reflex of the organic gardener. Mulch can be made up of various plant materials, all of which have many advantages: limitation of leaching of land by rains, reduction of watering needs in summer and in dry soil, improvement of soil fertility by better preservation of soil underground life (auxiliaries and micro-organisms).
In times of drought, the garden should be treated with horsetail and nettle manure and especially with biodynamic preparation 500.
3 IMPORTANT ASSETS IN SUMMER:
- hoeing, which offers a triple advantage:
- destroy weeds
- reduce soil evaporation
- maintain a soil structure which allows an increase in the microbial life of the soil, and therefore its fertility.
“one hoeing is worth two watering’s”
- watering:
- preferably water deeply and less often
- it is not recommended to water during hot hours
- avoid wetting the leaves of certain plants sensitive to powdery mildew
- in hot weather, watering is more beneficial in the evening.
- preferably use the rainwater collected because it is the best
- mulching:
- after superficial hoeing, mulch with wheat or oat straw or with leaves
- to retain the irrigation water and avoid the burning action of the sun’s rays, mulching is important
- Anything over 15 cm high can be mulched: all vegetables as well as flowerbeds and flower beds and ornamental shrubs.
- the straw should be cut with a straw chopper. Crushed and moistened, it decomposes faster and protects the soil better before becoming a source of humus
- if there is no straw, use shavings, sawdust, BRF, or dead leaves stored from one year to the next (or, if necessary, with cardboard sheets).
- green manures can also be used as protective plant cover.


Give a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.